
Acute Pain Nursing Diagnosis & Care Plan
Pain is a universal sensation that everyone experiences, and acute pain is a common reason why patients seek medical care. Nurses work with the interdisciplinary team to assess and manage pain in a multidimensional approach to provide comfort and prevent suffering. This chapter will review best practices and standards of care for the assessment and management of pain.
.png)
Acute pain nursing care plan Nursing Care Plan Examples
Assist the patient with frequent position changes at least every two hours and as needed. Lying or sitting in the same position for a long time may cause tense muscles, stiff joints, and pain at pressure points. Changing positions helps relieve pressure and reduce pain. Consider PCA if the patient is a candidate.
.png)
Acute pain nursing care plan Nursing Care Plan Examples
In the nursing care plan for acute pain: Identify and assess diverse causes of acute pain. Implement tailored interventions for effective pain relief. Promote overall comfort and functioning in individuals experiencing acute pain. Emphasize the importance of addressing underlying causes to prevent pain recurrence.
Ncp acute Pain Pain Pain Management
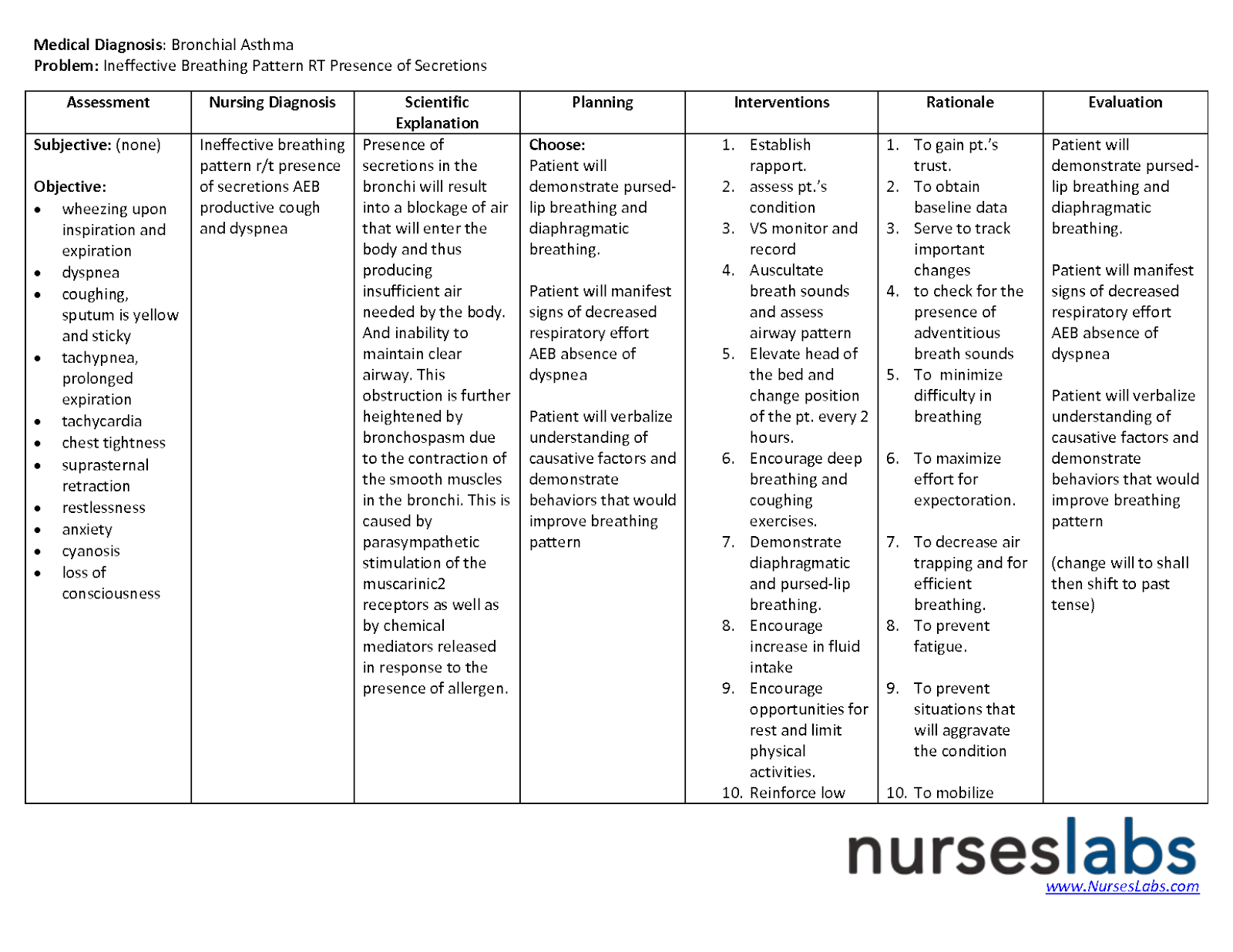
Acute Pain. Acute pain is an expected finding in appendicitis. Pain may start in the umbilical area and then shift to the right lower quadrant, becoming severe quickly. Nursing Diagnosis: Acute Pain. Related to: Inflammation ; Bloating/gas ; Ruptured appendix ; Infectious process ; As evidenced by: Complaints of sudden abdominal pain

Nursing Care Plan Acute Pain PDF Cough Breathing
The planning and implementation of a care plan for acute pain should be based on the patient's individual needs and preferences. The use of non-pharmacological interventions, such as relaxation techniques, distraction, and massage, can be effective in managing pain. Pharmacological interventions, such as analgesics, should be used as per the.
NCP Acute Pain PDF Pain Nursing
The following are the therapeutic nursing interventions for your acute pain nursing diagnosis: 1. Provide measures to relieve pain before it becomes severe. It is preferable to provide an analgesic before the onset of pain or before it becomes severe when a larger dose may be required.

Acute Pain Nursing Diagnosis & Care Plan Nurseslabs
Commonly used NANDA-I nursing diagnoses for pain include Acute Pain (duration less than 3 months) and Chronic Pain. See Table 11.5 for more information regarding these diagnoses. [3] For more information about defining characteristics and related factors for other NANDA-I nursing diagnoses, refer to a current nursing diagnosis resource.

Acute Pain Nursing Care Plan Nursing Care Plan Examples Images
These non-opioid nursing interventions for acute pain management include non-opioid pain relievers, complementary techniques, and non-medication strategies. Nurses must regularly assess pain and collaborate with both the patient and provider to ensure that timely access to adequate pain relief is a priority of their care..
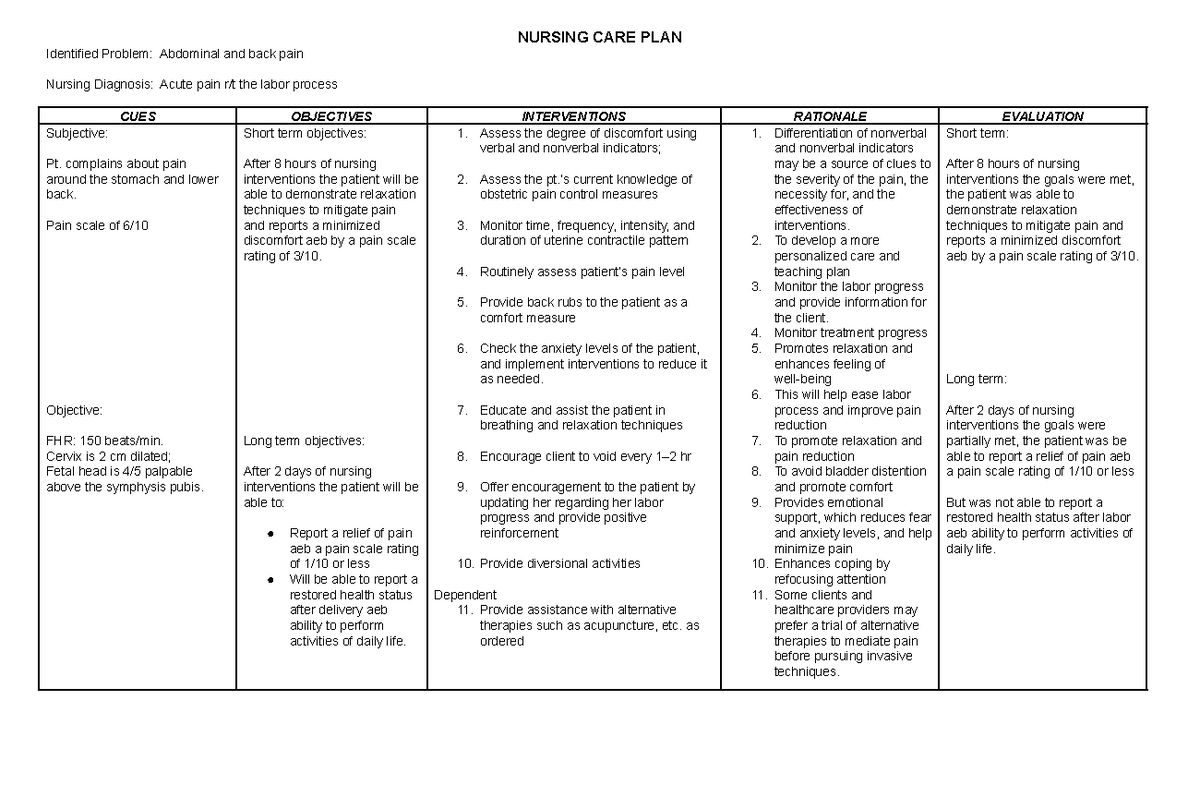
Acute Pain due to Labor Process NCP NURSING CARE PLAN Identified
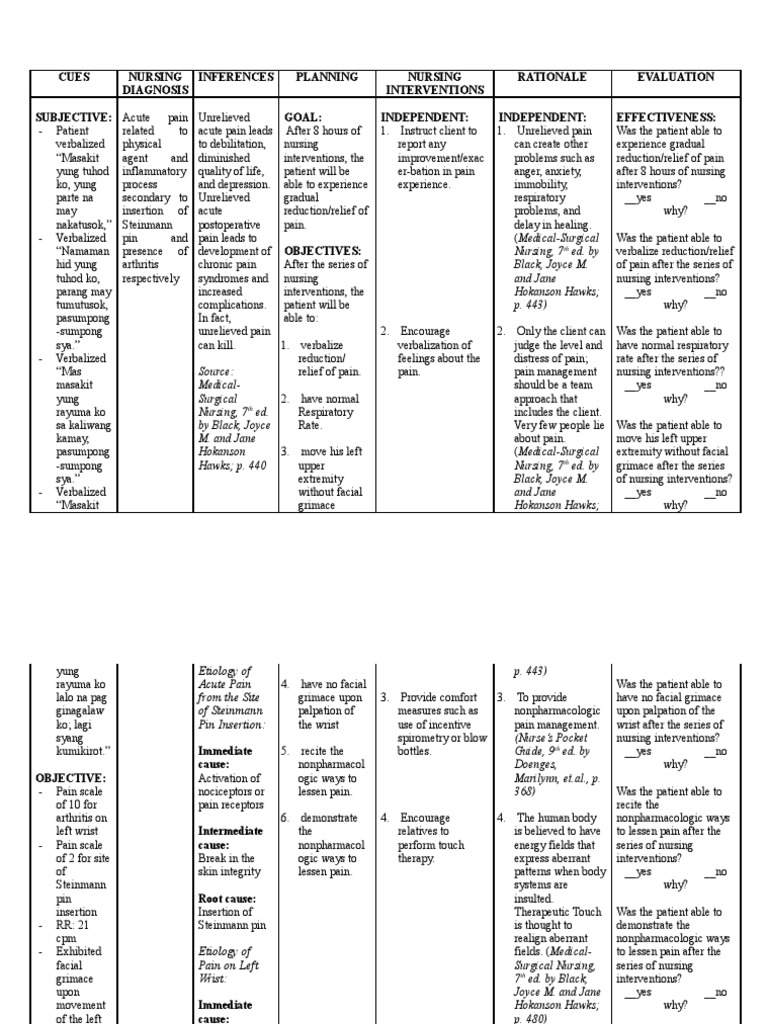
Nursing Diagnosis: Acute Pain related to traumatic injury secondary to spinal cord injury (SCI) as evidenced by extreme back pain, paraplegia, muscle spasm and severe headache. Desired Outcomes: The patient will report relief pain and discomfort. The patient will identify methods to manage pain.

SOLUTION Nursing care plan acute pain ncp Studypool
The following are assessment and nursing interventions for managing acute chest pain and discomfort: 1. Perform pain assessment: Identify precipitating events, if any, as well as frequency, duration, intensity, and location of the pain. This helps differentiate this chest pain and aids in evaluating possible progression to unstable angina.
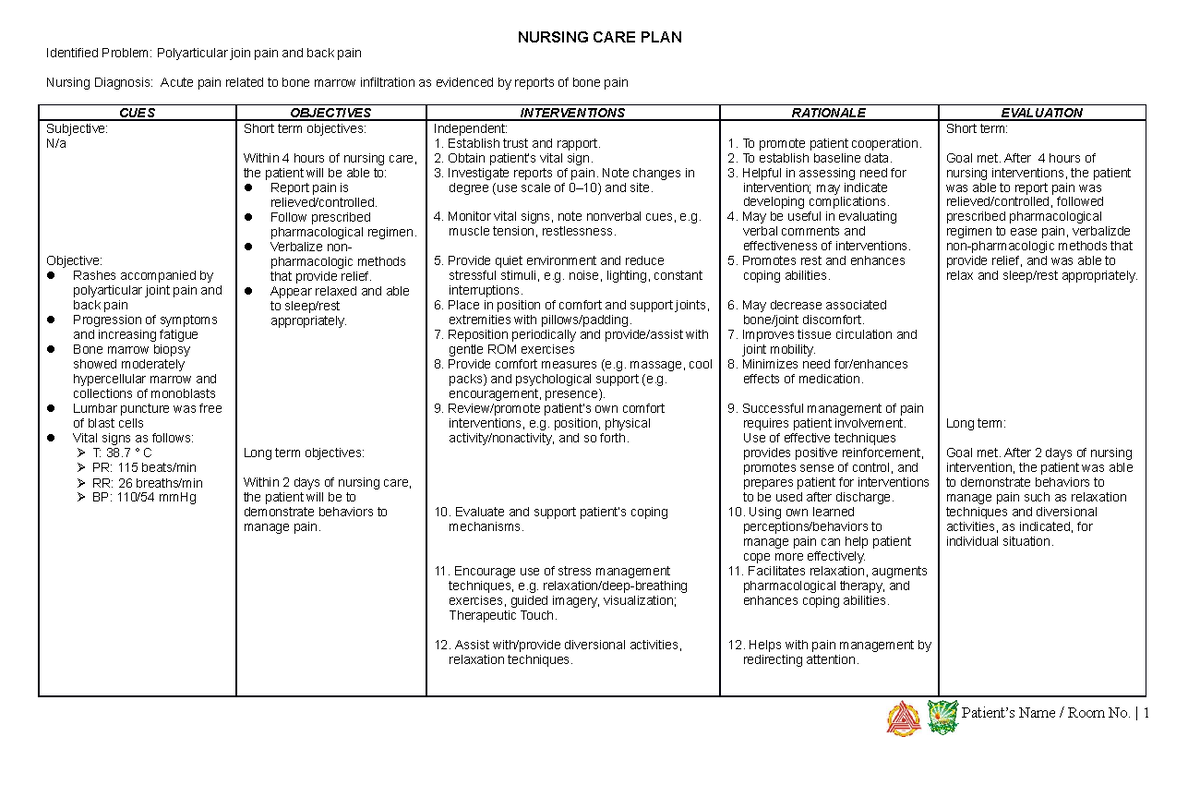
NCP1 nursing care plan acute pain BS Nursing MSU Main Studocu
A nursing diagnosis for Acute Pain is defined as an unpleasant emotional and sensory experience resulting from actual or potential damage to body tissue. It can be sudden or slow onset of any intensity, ranging from mild to severe, and can be experienced for a few seconds, up to 6 months. Chronic pain is defined as long-term pain experienced.
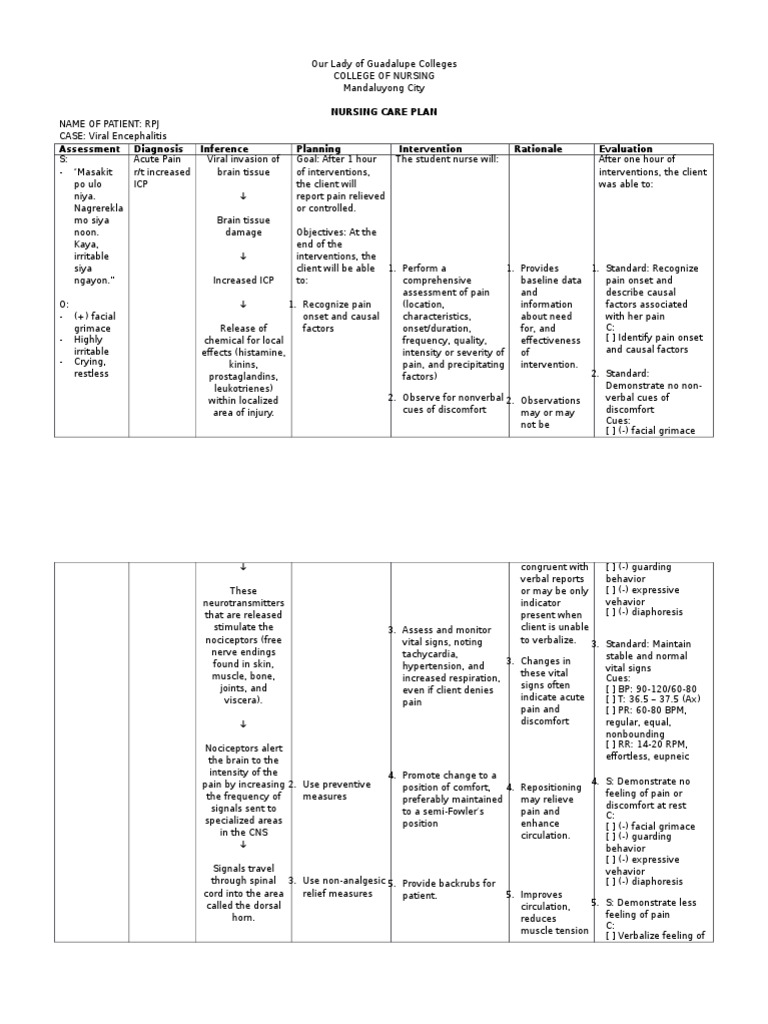
NCP Acute Pain Pain Symptoms And Signs
Acute pain can have a sudden or slow onset with an intensity ranging from mild to severe. It can happen after a medical procedure, surgery, trauma or acute illness. It has a duration of less than 6 months. Chronic pain. For pain to be classified as chronic, the patient needs to be experiencing it for more than 6 months.
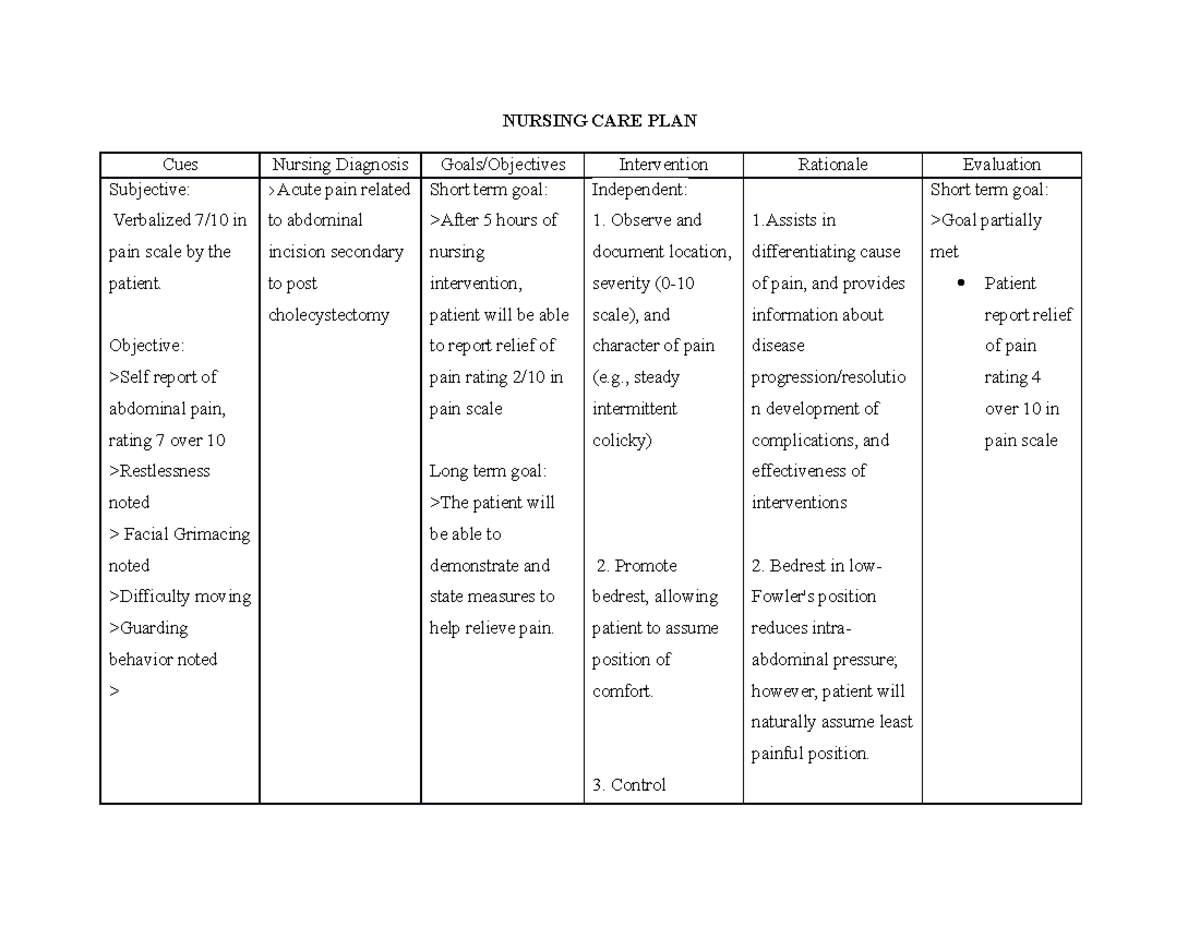
NCP (acute pain) Nursing Care Plan NURSING CARE PLAN Cues Nursing
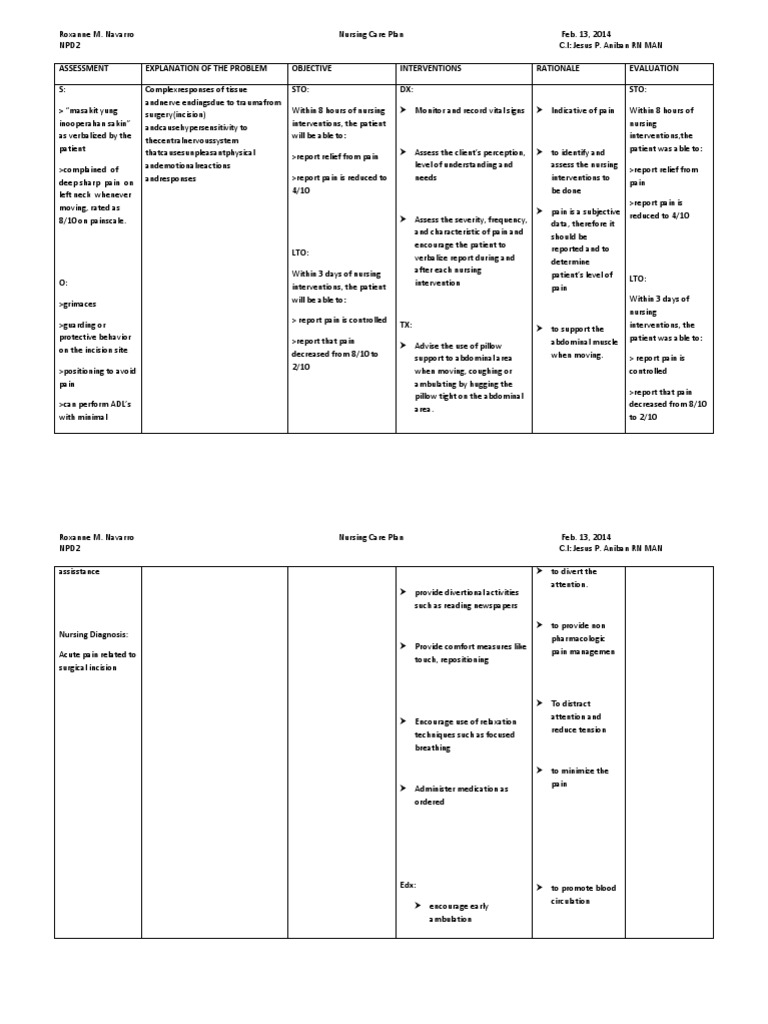
Nursing Diagnosis. Acute pain may be related to surgical incision; disruption of skin, tissue, and muscle integrity; musculoskeletal or bone injury; presence of tubes or drains as evidenced by verbal reports of pain, restlessness, crying, moaning, facial grimace, guarding, confusion, changes in vital signs.
.png)
Acute pain nursing care plan Nursing Care Plan Examples
Acute Pain Pathophysiology. Acute pain is a sudden discomfort that typically lasts three to six months. It can serve as a warning of disease, illness, or traumatic event. Some examples include: a burn, cut, or broken bone. Acute pain might be mild and last just a moment, or it might be severe and last for weeks or months.
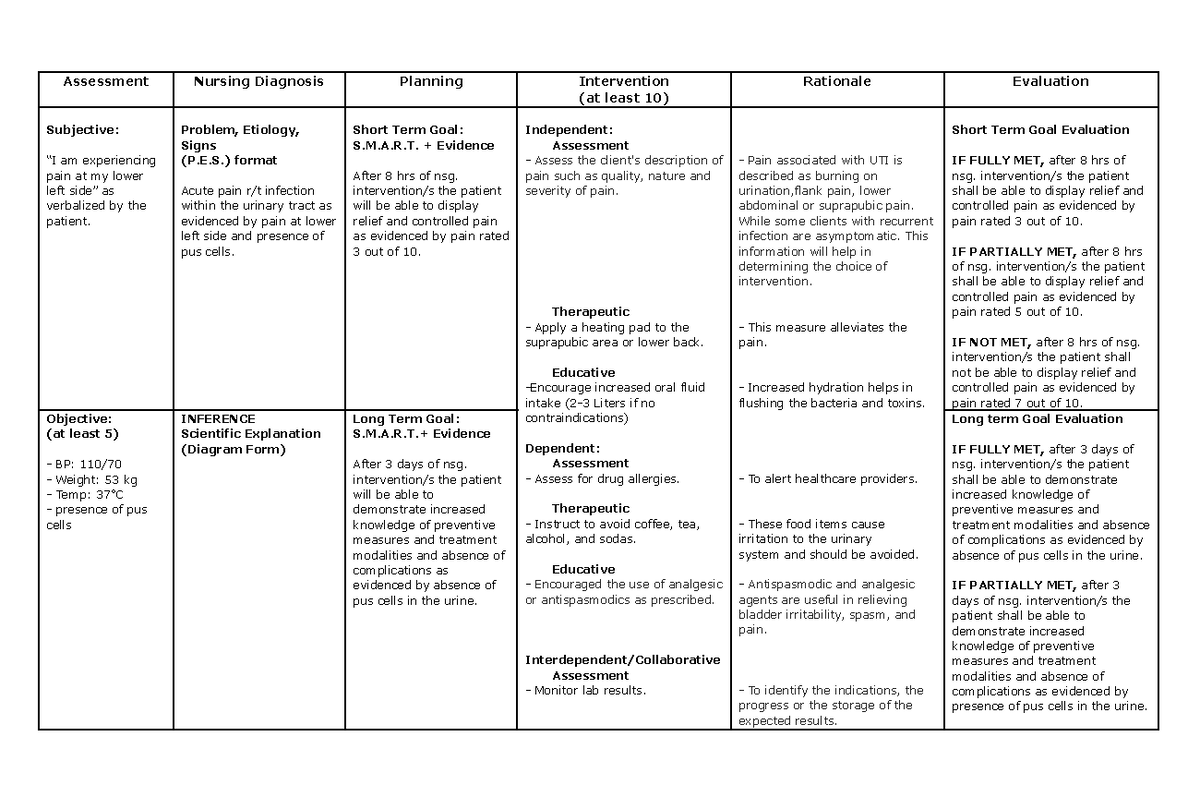
NCP Acute pain Assessment Nursing Diagnosis Planning Intervention (at
Provide medication at regular intervals; titrate to patient response; premedicate for painful procedures. Manage breakthrough pain with additional doses; consider rotation or switching medication. Monitor for signs of substance tolerance (increased dose to reach desired effect, decreased effect with same dose).
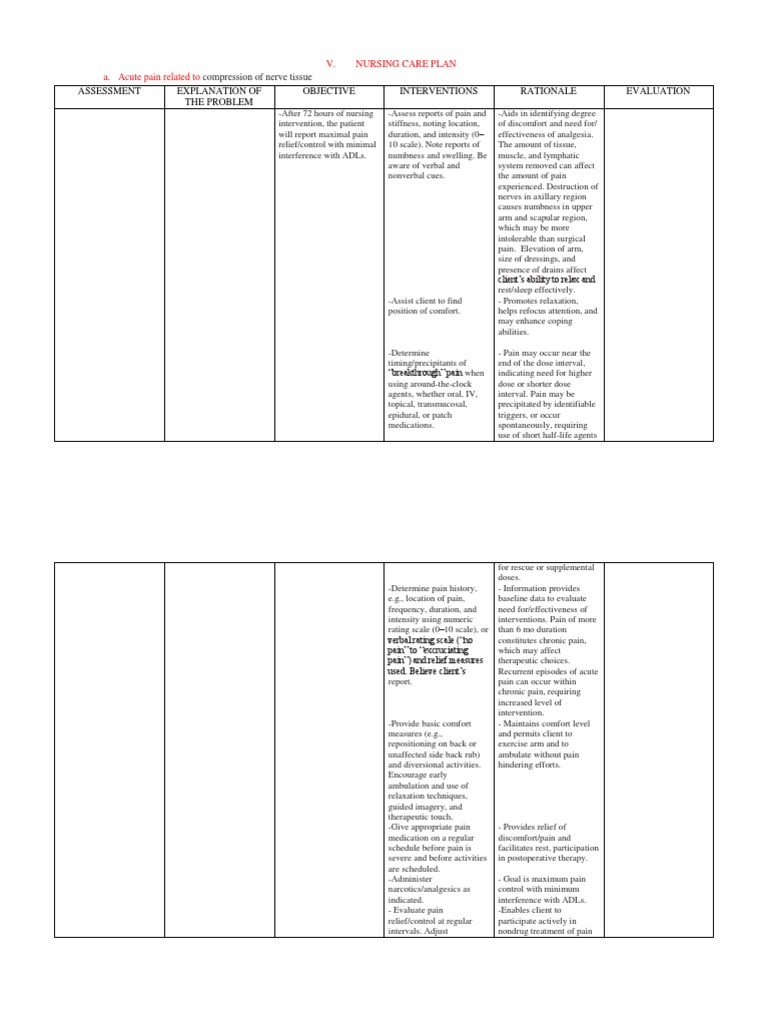
Nursing Care Plan acute pain Pain Pain Management
Acute pain is defined as an unpleasant emotional and sensory experience. It is most often associated with damage to the body's tissues. The onset of acute pain can be slow or sudden. The main difference between acute and chronic pain is that acute pain has an anticipated resolution lasting less than three months.